In fact the National Child Traumatic Stress Network shares Early childhood trauma has been associated with reduced size of the brain cortex. Developmental trauma or trauma that happens during early childhood can significantly impact a persons ability regulate emotion and behavior.
 Allison Davis Maxon On Twitter Childhood Trauma And Brain Development Children Learn What The Live Childtrauma Fostercare Adoption Kinship
Allison Davis Maxon On Twitter Childhood Trauma And Brain Development Children Learn What The Live Childtrauma Fostercare Adoption Kinship
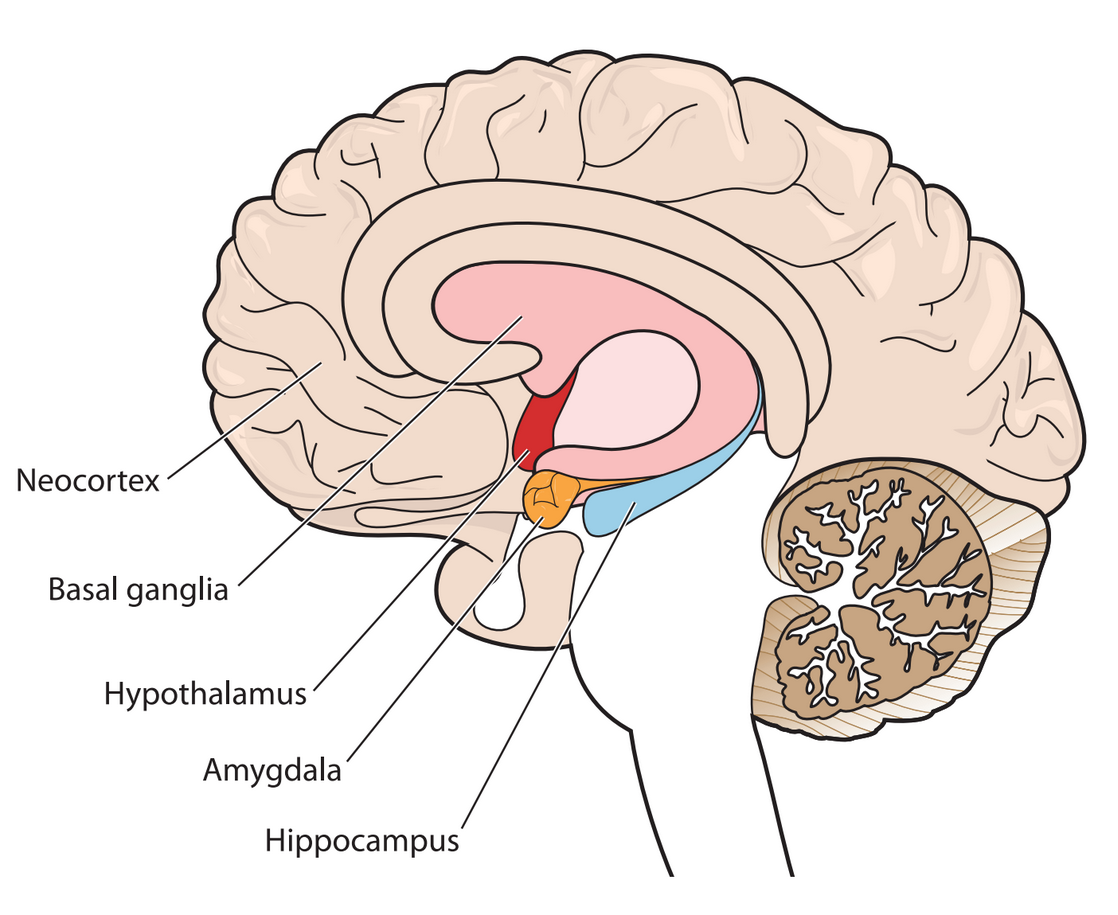
Trauma can thus cause lasting changes in the areas of the brain that deal with stress namely theamygdala hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.

How does childhood trauma affect the brain. Research has shown that survivors of childhood trauma have reduced volume in the hippocampus. Seen in children who have experienced trauma. Children may be more impacted by trauma than adults but providing them treatment early on can minimize the effects.
As a result children who experience trauma may not be able to retain information about how to tell if one situation is safe and. How childhood trauma affects the brain It is not news that people abused as children are more exposed to clinical depression anxiety and a higher risk of death from. They are experience-dependent and these experiences are apparently encoded.
The three main parts affected by trauma are the amygdala the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex. How Trauma Affects Children. This area is responsible for many complex functions including memory attention perceptual awareness thinking language and consciousness Additionally the childs IQ and ability to regulate emotions suffers.
Many people experience trauma early on in life while their brain is still developing. The insula is a region of the brain buried deep in the cerebral cortex that is crucial for self-awareness and reactions to sensory information. This area of the brain is critical for learning memory formation conflict processing emotional regulation and and even establishing social.
Studies on animals also found that trauma actually damaged neurons. Being constantly on alert and unable to relax no matter the situation Feeling fearful most or all of the time. PTSD is a mental health condition that can impact children in different ways.
Coping with trauma has multiple physical emotional and psychological effects and can have severe effects on the brain as well. Because childhood abuse neglect and trauma change brain structure and chemical function maltreatment can also affect the way children behave regulate emotion and function socially. Boys with trauma had larger insula volume and surface area than boys in the control group while girls with trauma had smaller insula volume and surface area than girls in the control group.
It also alters memory. Early childhood trauma has been associated with reduced size of the brain cortex. This area is responsible for many complex functions including memory attention perceptual awareness thinking language and consciousness.
Some children find themselves replaying the traumatic incident in their minds relieving the stress and agony. Its highly impacted by stress. Children with post-traumatic stress will have variations in the volume and surface area of the insula.
According to the National Center for PTSD up to 15 of girls and 6 of boys develop PTSD following a traumatic event. These potential effects include. Trauma likely impacts a variety of types of learning and memory such as the ability to learn and remember information about the surrounding environment.
This suggests that trauma may affect how the hippocampus develops. The brain and especially its spontaneous activity are highly sensitive to experiences in the environment. Young children who experience trauma are at particular risk because their rapidly developing brains are very vulnerable.
In adult survivors of childhood sexual abuse the hippocampus tends to be smaller3 Survivors often have difficulties with memories and experience flashbacks. As stated above childhood trauma affects the way your neural pathways form or do not form. The hippocampus helps you form memories and learn new information.